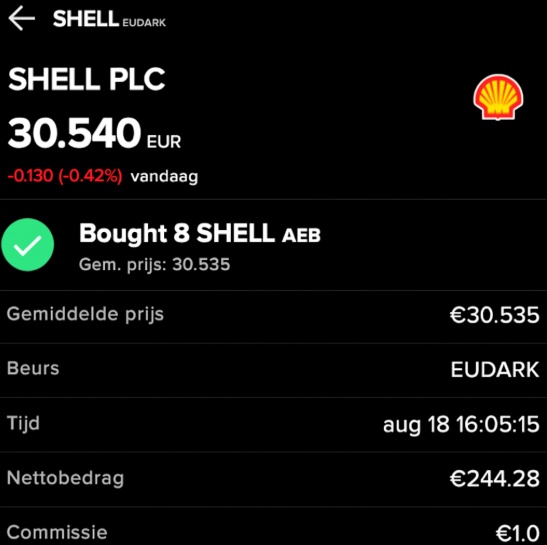
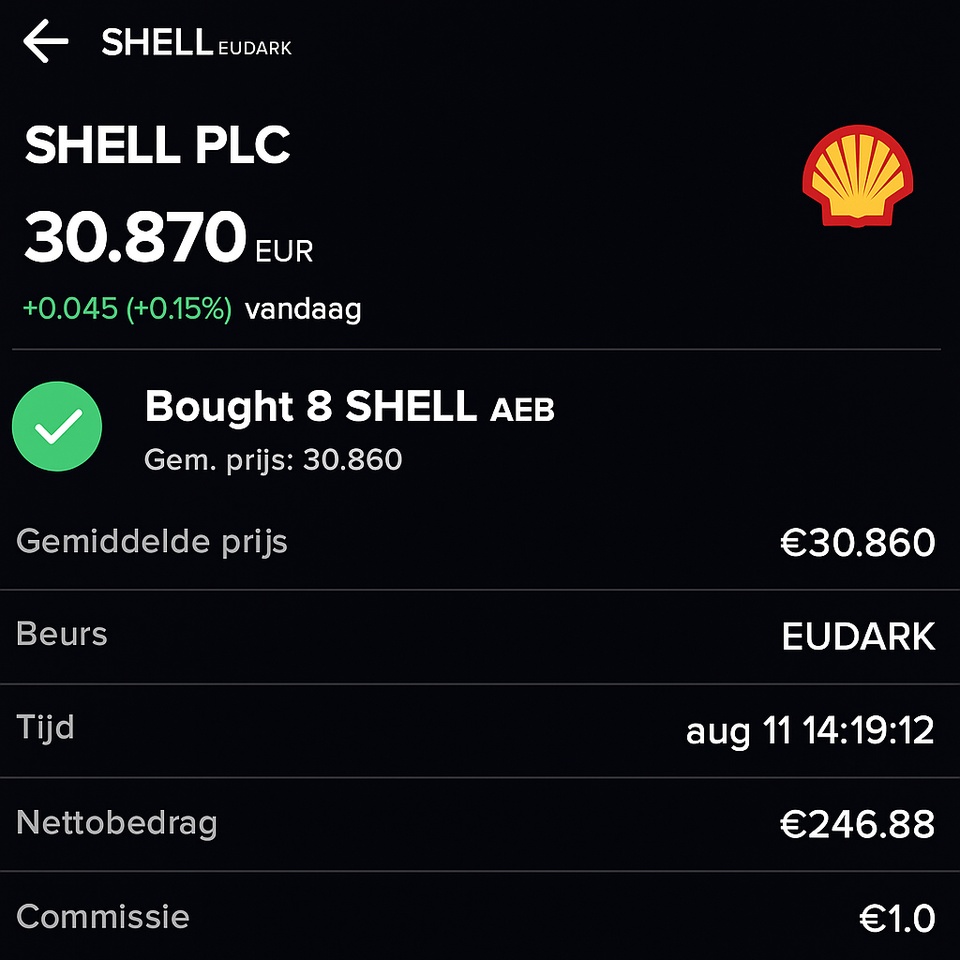
With my KI-gestützten DCF-Prompt I have analyzed several stocks from my portfolio that are currently trading well below their all-time highs.
The results are not binding buy or sell signals, but merely an additional building block in the decision-making process. All information is of course provided without guarantee.
🤖 All analyses were carried out with Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Research created.
On average, each analysis researched 223 websites.
As the full reports are very extensive, the appendix contains only
- the fair values for bull, base and bear cases
- a compact summary of the most important findings
📍Lockheed Martin $LMT (-0,76%)
Current share price August 4, 2025: $421
Fair value
Bull: $570.80
Base: $495.50
Bear: $425.20
Lockheed Martin is at a critical juncture. The share price reflects deep concerns over repeated multi-billion dollar write-downs on risky fixed-price development programs, which peaked in the second quarter of 2025. Our analysis yields a fair value of USD 495.50, well above the current price, and a range of USD 425 to USD 571 in our scenarios.
The key value drivers are the record high order backlog of over USD 166bn, the strong demand for tactical missiles (MFC) and the stability of the space business (Space), which form a solid base.
The greatest leverage lies in management's ability to stabilize operational execution in the Aeronautics segment and normalize margins.
The main risks remain further unforeseen losses on classified programs, the high focus on the F-35 program and the volatility of US defense budgets. The current valuation provides a significant margin of safety for investors who believe in a stabilization of operational performance and the long-term strategic importance of the company.
📍Chevron $CVX (-0,65%)
Current price August 4, 2025: $151
Fair value
Bull: $203.80
Base: $178.50
Bear: $155.20
The comprehensive DCF analysis results in a fair value of USD 178.50 per share for Chevron, which implies a significant undervaluation compared to the current share price. The valuation range from the scenarios (USD 155.20 - 203.80) and the Monte Carlo simulation supports this assessment and shows a limited downside risk even in the bear scenario.
The key value drivers are the transformative Hess acquisition, which heralds a new era of high-margin growth, and the impressive capital and cost discipline, which manifests itself in rising free cash flow. These factors position Chevron robustly to benefit disproportionately from a stable or rising energy price environment.
The main risks remain the exogenous volatility of the commodity markets and the operational execution of the integration of Hess and the ramp-up of major projects. Overall, the opportunities resulting from the strategic realignment and the attractive valuation clearly outweigh the inherent risks in the sector.
📍Occidental $OXY (-0,43%)
Current share price August 4, 2025: $43
Fair value
Bull: $79.8
Base: $64.1
Bear: $51.5
The comprehensive DCF analysis results in a fair value of $64.1 per share for Occidental Petroleum, which corresponds to a considerable upside potential compared to the current price of $43.41. The valuation range resulting from the scenarios and simulations is between $51.5 and $79.8.
The key drivers for this value are the robust free cash flow from the scaled and highly efficient Permian Basin business and the disciplined capital allocation, which prioritizes debt reduction and thus increases shareholder value. The main risks remain the inherent volatility of commodity prices and the significant execution and political risks associated with the ambitious but as yet unproven low carbon ventures strategy.
Based on the significant discrepancy between the calculated fair value and the current market price, a buy recommendation is issued for Occidental Petroleum shares. Investors should closely monitor the development of commodity prices, the progress in deleveraging and the operational and commercial milestones of the LCV division, in particular the STRATOS project.
📍Intel $INTC (-7,3%)
Current share price August 4, 2025: $19
Fair value
Bull: $36.10
Base: $25.20
Bear: $15.50
Based on a detailed discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis using the sum-of-the-parts method (SOTP), Intel Corporation has a fair value of $25.20 per share in the base scenario. This implies an upside potential of 27.3% compared to the reference price of $19.80. The valuation range derived from the bull and bear scenarios ranges from $15.50 to $36.10 per share. The Monte Carlo simulation, which takes a probabilistic view of the uncertainties of the central assumptions, yields a median value of $24.50 and indicates that the share is trading below its fair value with a probability of around 68%.
The investment thesis for Intel is a high-risk turnaround bet that is inextricably linked to the success of the "IDM 2.0" strategy and in particular the development of the Intel Foundry (IF) business. The primary value drivers are management's ability to win one or more "significant" external foundry customers, the stabilization of market share in the core Client Computing (CCG) and Data Center & AI (DCAI) businesses and the realization of the announced cost reductions.
The main risks lie in the enormous challenge of mastering the turnaround in the established segments and at the same time building up a world-class foundry business from a position of being behind. Persistent operating losses and cash outflows from the foundry business, further loss of market share to agile competitors such as AMD and Nvidia and the failure to regain technological leadership in process technologies by 2025 represent existential risks that could turn the massive capital investments into value-destroying stranded assets.
📍Nutria $NTR (+0,65%)
Current share price August 4, 2025: $58
Fair value
Bull: $90
Base: $68.2
Bear: $45
This analysis provides a detailed fundamental valuation of Nutrien Ltd (Nutrien) based on a discounted cash flow (DCF) model. The base case scenario yields a fair value of USD 68.2 per share (equivalent to CAD 93.8). The valuation range determined by scenario analyses and a Monte Carlo simulation indicates a balanced risk-return profile.
The central investment argument is based on Nutrien's position as an integrated global market leader in an industry with positive long-term fundamentals. The valuation suggests that the stock is currently fairly valued but offers potential from an expected recovery in fertilizer prices and margins from their cyclical lows.
Key value drivers include operational efficiency reinforced by the integrated business model (production and retail), disciplined capital allocation with a focus on shareholder returns and the underlying strength of global agricultural markets supported by low grain inventories.
The main risks lie in the inherent volatility of commodity prices, exposure to the cost of key inputs such as natural gas in the nitrogen segment and geopolitical uncertainties that may impact global supply chains. A key uncertainty factor for the short-term forecast is the strong dependence on a significant increase in earnings in the second half of 2025 in order to achieve the company's forecast after a weak first quarter.