Shares in $LYFT (+0.18%)
are in high demand. In pre-market trading in the US, they soared by a whopping 30 percent. Background: Google's parent company Alphabet wants to launch its Waymo robotaxi service next year in collaboration with the ride-hailing company in Nashville. This would be the first commercial use of Waymo's driverless cabs in the Lyft network, which also wants to invest in a facility to maintain Waymo vehicles. Waymo is thus increasing the pressure on rival Tesla, which launched its own robotaxi service in Austin in June. Lyft shares recently traded 14 percent higher.
Discussion about LYFT
Posts
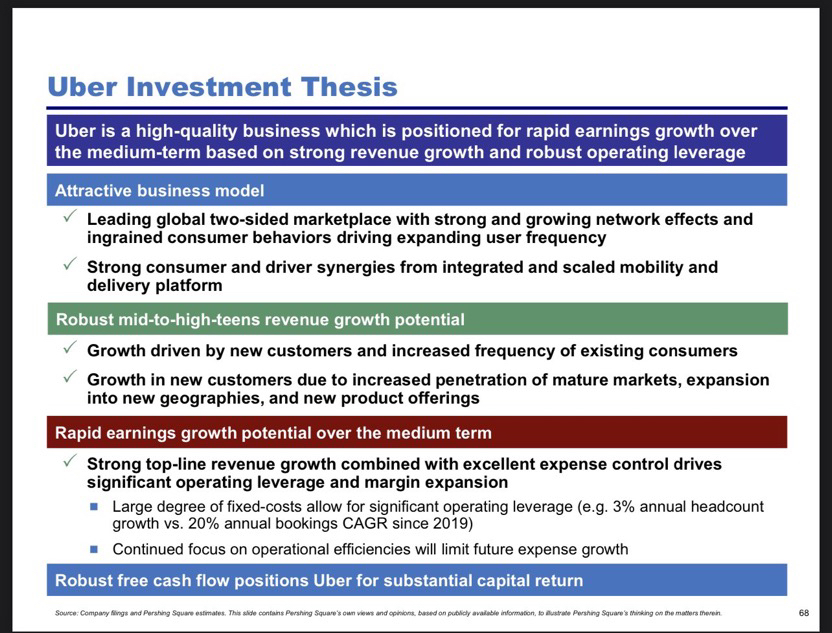
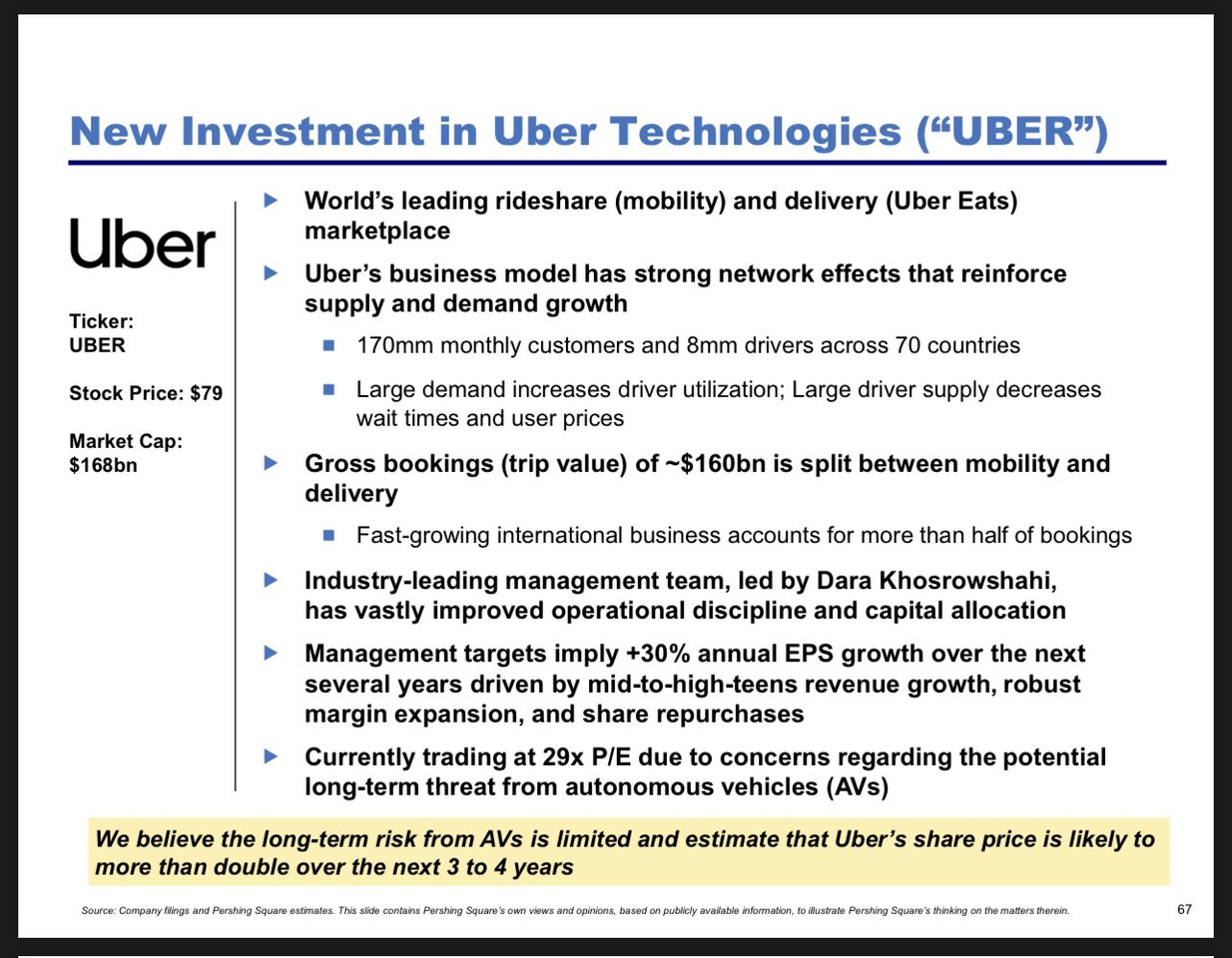
26Robotaxi cooperation causes Lyft share price to explode

Robotaxis and autonomy - the billion-strong ecosystem behind the cars - IAA 2025
Hello dear Getquin Community,
This year's IAA Mobility in Munich showed that the automotive industry is on the verge of a turning point. With over 30 percent more exhibitors than in 2023 and numerous premieres from Audi, $BMW (+0.78%) BMW, $MBG (+0.68%) Mercedes, $VOW3 (+0.96%) VW, Opel and Chinese challengers such as BYD and $1211 (-0.43%) BYD and $9868 (+1.55%) XPeng, it became clear that electromobility has now become the standard. However, behind these new platforms and concepts lies an even bigger topic, namely autonomous driving and the robotaxis of the future.
In order to present this field in a clear and transparent way for investors, I have broken down the entire value chain into individual sectors. These include automotive and suppliers, semiconductors and technology, communication and infrastructure, software and algorithms, logistics and transportation, insurance and finance, energy and infrastructure, battery and propulsion, maps and mapping, and safety and cybersecurity. Within each sector, I have analyzed the big players, the hidden champions and the blade manufacturers and highlighted my favorites in each case with a brief explanation. @Multibagger 😎
My aim was to develop as comprehensive a picture as possible that shows where the opportunities lie in this new industry and how investors can position themselves at an early stage. Perhaps the IAA 2025 was not just a car show, but actually the starting signal for the next big investment ecosystem around robotaxis and autonomous driving. If I have overlooked any important aspects or if a categorization was not quite precise, I look forward to your comments @BamBamInvest
@Epi
😎 and exciting additions @All-in-or-nothing 😎 Together we can understand this topic even better and learn from each other. @Tenbagger2024 😎
Feel free to leave a 👍. I wish you every success with your investments 🚀
🚘 Automotive & suppliers
Big player:
$TSLA (-2.95%) Tesla - pioneer in autopilot/FSD, vertical integration, huge database
$MBG (+0.68%) Mercedes-Benz Group - EQS/EQE with Level 3 approval in Germany, strong regulatory expertise
$BMW (+0.78%) BMW - New class platform, e-models with prepared sensor technology & level 3 approaches
$VOW (+1.73%) VW Volkswagen - Cariad software unit, massive push towards ADAS/AV
$7203 (+0.42%) Toyota (Japan) - largest OEM, cooperation with Pony.ai and Denso
$GOOGL (+2.27%) Alphabet Waymo (private/Alphabet $GOOGL) - robotaxi pioneer in the USA
$9888 (+1.8%) Baidu Apollo (9888.HK) - Robotaxi & Full-Stack AV in China
$Pony.ai (private, China) - Robotaxi & partnerships with Toyota
👉 Favorite: Alphabet Waymo ($GOOGL (+2.27%))
Moat through years of data collection in real operation, deep AI integration, financially secured by Alphabet. Compounder potential, as Waymo can scale as a platform.
Hidden champions:
$APTV (+0.68%) Aptiv - supplier for ADAS, sensor fusion, E/E architectures
$MG (-0.01%) Magna International - produces complete vehicle systems including autonomous components
$ZF Friedrichshafen (private) - German giant in steering and braking systems for AVs
Veoneer (private, formerly listed) - safety software, vision, sensor technology
$SHA0 (+1.16%) Schaeffler AG (DE, Germany, Xetra) - global supplier of drive, chassis and intelligent steering systems. Important for e-mobility and redundancy solutions in autonomous driving.
👉 Favorite: Aptiv ($APTV (+0.68%)
)
High barriers to entry through system integration, broad customer base (OEM-agnostic), strong cash flow and close partner of major car manufacturers.
Blade manufacturer:
$NVDA (+1.48%) Nvidia - Drive Orin / Thor chips for OEMs, standard in the AV sector
$QCOM (+0.42%) Qualcomm - Snapdragon Ride platform for AVs
$INTC (-6.42%) Intel Mobileye - EyeQ chips, one of the market leaders in ADAS
$LAZR (+28.89%) Luminar Technologies - Lidar, partnerships with Volvo, Mercedes, SAIC
$OUST Ouster, Inc. - Lidar solutions
$INVZ Innoviz (INVZ) - Lidar sensor technology, cooperation with VW & BMW
👉 Favorite: Nvidia ($NVDA (+1.48%)
)
Dominance in high-performance AI chips, ecosystem with software (CUDA, DriveSim), network effects through partnerships with almost all OEMs. Classic compounder, enormous moat due to technology and developer lock-in.
Takeaway:
In the automotive & supplier sector, it's not just who sells the most cars, but who has mastered the best technology stack for autonomy. OEMs work closely with specialized suppliers and blade manufacturers. Investors should focus less on unit numbers and more on data basis, software expertise and partnerships. The real levers often lie with suppliers and technology enablers, not just the traditional car brands.
💻 Semiconductors & technology
Big players:
$NVDA (+1.48%) Nvidia - GPUs & AV chips (Drive Orin, Drive Thor), software ecosystem
$QCOM (+0.42%) Qualcomm - Snapdragon Ride platform, automotive pipeline >30 billion USD
$INTC (-6.42%) Intel / Mobileye - EyeQ chips, ADAS market leader
$AMD (+5.41%) AMD - GPU/CPU, entry into automotive AI compute
👉 Favorite: Nvidia ($NVDA (+1.48%)
) Unique position: Technological moat through CUDA ecosystem, enabler of almost all AV developments, quasi-monopoly in high-end compute. Classic compounder with long-term growth leverage.
Hidden champions:
$LAZR (+28.89%) Luminar Technologies - Lidar supplier, partnerships (Volvo, Mercedes, SAIC)
$INVZ Innoviz Tech. - Lidar, BMW & VW as customers
$KOTMY Koito Manufacturing - world market leader in automotive lighting, entry into lidar through Cepton integration, important role as supplier for OEMs
$AMBA (+2.91%) Ambarella (AMBA) - camera chips & vision processors for AV
$STMPA (-2.52%) STMicroelectronics (France/Italy, Euronext) - automotive microcontrollers, sensors, power electronics. European counterpart to Infineon.
$AIXA (+1.64%) Aixtron (Germany, Xetra) - supplies manufacturing equipment for SiC and GaN semiconductors, indispensable for power electronics in EV/AV.
$ELG (+3.07%) Elmos Semiconductor (Germany, Xetra) - niche player for mixed-signal semiconductors in automotive, e.g. for radar and driver assistance.
👉 Favorite: Luminar ($LAZR (+28.89%)
) Clear technical USP, strategic OEM deals in series production, high barriers to entry in lidar technology. Scalable compounder in a niche market.
Blade manufacturer:
$TSM (+1.6%) Taiwan Semiconductor - production of all relevant automotive chips
$ASML (+0.42%) ASML Holding - Lithography monopolist, without ASML no AI/AV chips
$EQIX (+1.3%) Equinix - data center colocation for AI training & simulations
$DLR (+2.59%) Digital Realty - cloud and data infrastructure
$AMZN (+1.99%) Amazon AWS - Cloud resources for AI training, simulation & OTA updates
👉 Favorite: ASML ($ASML (+0.42%)
) Monopoly on EUV lithography, no advanced chips for autonomous driving without ASML. Moat through technology and patents, classic compounder.
Takeaway:
Semiconductors & technology are the foundation of autonomous driving. While Nvidia plays the central role with computing power, lidar specialists such as Luminar ensure perception. The real shovelware winner, however, is ASML, without whose machines there would be no AV chips. Investors will find the deepest technological moats in the entire value chain here.
📡 Communication & infrastructure
Big players:
$ERIC B (-0.22%) Ericsson - 5G/6G networks, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) applications, global player
$NOK (+1.89%) Nokia - 5G/Edge solutions for automotive & smart cities
$QCOM (+0.42%) Qualcomm - Snapdragon Digital Chassis, V2X chipsets, automotive pipeline
Huawei (private, China) - strong player in 5G/AV communication, partnerships in Asia
👉 Favorite: Qualcomm ($QCOM (+0.42%)
) Wide moat through IP in mobile communications, at the same time deep automotive integration via Snapdragon Ride & Digital Chassis. Compounder, as economies of scale in chips + licenses worldwide.
Hidden champions:
$Cohda Wireless (private, Australia) - pioneer for V2X communication, software solutions for OEMs
$Autotalks (private, Israel, acquisition by Qualcomm planned) - leader in dedicated V2X chips
Commsignia (private, Hungary) - V2X middleware & roadside units
👉 Favorite: Autotalks (private, Israel)
Technology leader in dedicated V2X chips, unique IP portfolio. Strong takeover candidate (Qualcomm already active), giving moat + exit potential.
Shovel manufacturer:
$CSCO (+0.11%) Cisco Systems - network infrastructure for automotive, cloud & edge
$AMT (+0.37%) American Tower - cell towers & infrastructure, benefits from 5G expansion
$CCI (-0.19%) Crown Castle - radio tower and fiber optic infrastructure (mainly USA)
$EQIX (+1.3%) Equinix - data centers, basis for edge computing and OTA updates
$DLR (+2.59%) Digital Realty - colocation & data center capacity for simulations and AV data
👉 Favorite: Equinix ($EQIX (+1.3%)
)
Global leader in data center colocation, benefits from the edge computing trend. Strong moat due to network effects & high switching costs. Long-term compounder.
Takeaway:
Communication & infrastructure are the silent cornerstones of autonomous driving. Without low-latency networks, edge data centers and V2X communication, no AV can drive safely. While Qualcomm forms the technological bridge between chip and infrastructure, hidden champions such as Autotalks secure niche leadership. On the blade side, Equinix remains unbeatable, as every OEM & service provider needs computing power at the edge.
🤖 Software, platforms & algorithms
Big Player:
$GOOGL (+2.27%) Alphabet / Waymo - Robotaxi pioneer, full-stack AV software, years of database
$TSLA (-2.95%) Tesla - FSD, Dojo supercomputer, vertical integration incl. fleet
$9888 (+1.8%) Baidu Apollo (HK) - largest robotaxi network in China, full-stack solution
$UBER (+0.05%) Uber - AV platform in partnership (e.g. with Momenta), scaling via existing user base
👉 Favorite: Alphabet / Waymo ($GOOGL (+2.27%)
)
Unbeatable moat due to millions of real driving kilometers + simulations, strong financial base via Alphabet, focus on platform scaling (robotaxi, licensing model). Compounder with global expansion potential.
Hidden champions:
$Momenta (private, China) - L4 software for OEMs, partner of Mercedes, Toyota
$AUR Aurora Innovation - software + sensor technology for truck autonomy, partner PACCAR, Volvo
$Argo AI (private, USA) - formerly Ford/VW, now partly continued through partner projects
$Oxbotica (private, UK) - modular AV software, focus on industrial & logistics applications
👉 Favorite: Aurora Innovation ($AUR
)
Clear focus on trucking (biggest lever in the AV market), long-term OEM partnerships, strong moat due to specialization in long-haul autonomy. Still young, but strong compounder potential.
Shovel manufacturer:
$PLTR (+2.35%) Palantir - data management, simulation & AI analysis for AV training
$SNOW (+1.87%) Snowflake - Cloud data platform, relevant for AV data streams
$MSFT (+0.62%) Microsoft Azure - cloud & simulation platform for OEMs
$AMZN (+1.99%) AWS - largest provider for AI training & simulations in the AV sector
$ADBE (+0.24%) Adobe - Simulation & Digital Twin Tools (via partnerships)
👉 Favorite: Palantir ($PLTR (+2.35%)
)
Deep integration in data pipelines, modular platform for simulation & decision logic. Moat due to lock-in effects with major customers, strong compounder with AI scaling.
Takeaway:
Software and algorithms are the real key to autonomous driving. Vehicles are becoming "data centers on wheels" and only the companies with data, simulation and AI stacks can dominate the market in the long term. Waymo provides the scalable robotaxi ecosystem, Aurora scores with its trucking focus, and Palantir ensures that data streams remain manageable. This is where the biggest margins are generated, not in the sale of hardware.
🚚 Logistics & transportation
Big player:
$AUR Aurora Innovation - focus on autonomous trucks, partnerships with Volvo & PACCAR
$TuSimple (private, USA) - pioneer for autonomous trucks, strong in the USA and China, currently undergoing restructuring
$AMZN (+1.99%) Amazon / Zoox - Robotaxi & autonomous delivery services, integration into e-commerce and Prime
$FDX (+0.8%) FedEx - test programs for autonomous delivery (cooperations with Aurora, Nuro, among others)
$DHL (-0.15%) Deutsche Post DHL - pilot projects with autonomous delivery vehicles & drones
👉 Favorite: Amazon / Zoox ($AMZN (+1.99%)
)
Moat through e-commerce ecosystem, integration of AV in the last mile, strong financial power and scalability. Compounder due to synergies between logistics and technology.
Hidden champions:
$Nuro (private, USA) - autonomous delivery vehicles specifically for the last mile
$Einride (private, Sweden) - electric autonomous trucks, focus on freight & sustainability
$Gatik (private, Canada/USA) - AV for medium distances (B2B supply chains, e.g. Walmart)
$Starship Technologies (private, Estonia/USA) - autonomous delivery robots for urban logistics
👉 Favorite: Gatik (private, Canada/USA)
Clear business model: "middle-mile" logistics, profitable niche market with predictable routes. Moat through early commercial contracts (Walmart). Compounder potential through scaling in the B2B sector.
Shovel manufacturer:
$CAT (+0.84%) Caterpillar - autonomous technologies for construction machinery & mining, know-how transferable
$DE (+0.42%) Deere & Co - autonomous agricultural machinery, similar technology stacks as for trucks
$ISRG (-0.35%) Intuitive Surgical - example of high-end automation (here as a cross-reference for AV tech transfer)
$UPS (+0.52%) United Parcel Service - logistics infrastructure, partner for AV integration
$R (+1.81%) Ryder System - fleet management, leasing and AV test integration
👉 Favorite: Deere & Co ($DE (+0.42%)
)
Autonomy already in use (precision farming), moat through data & technology in the agricultural sector. Compounder quality, as know-how in navigation & autonomy is transferable to transportation/logistics.
Takeaway:
Logistics is one of the first markets where autonomous driving brings real profitability. Trucks and delivery services benefit from 24/7 operation without drivers, while the last mile (Nuro, Gatik) opens up new business models. Amazon is the most powerful player through vertical integration, while hidden champions like Gatik occupy targeted profitable niche markets. Shovel manufacturers such as Deere supply the already proven autonomy stacks.
🏦 Insurance & finance
Major players:
$ALV (+0.33%) Allianz - the world's largest insurer, involved in AV pilot projects at an early stage
$MUV2 (+0.48%) Munich Re - reinsurance, develops models for AV risk transfer
$CS (+0.18%) Axa - active in AV insurance testing & research
$BRK.B (+0.28%) Berkshire Hathaway - large presence in the US motor insurance market via Geico
👉 Favorite: Munich Re ($MUV2 (+0.48%)
)
Moat through global reinsurance strength, pioneer in new risk models for AVs. Compounder characteristics through diversification and ability to insure new markets (cyber, AV, climate) at an early stage.
Hidden champions:
$LMND (+0.69%) Lemonade - digital insurance, AI-driven, quickly adaptable for AV policies
$Root Insurance (private/USA, formerly listed) - data-driven car insurance, use of driving data
$Next Insurance (private, USA) - platform approach, simple onboarding for new risks
$Wefox (private, Germany) - digital platform for insurance brokerage, flexible for new products
👉 Favorite: Lemonade ($LMND (+0.69%)
)
Pure digital insurer with AI-driven underwriting. Moat through data and automation approach. Still small, but compounder potential as scalable platform can be used in new markets such as AV policies.
Shovel manufacturer:
$SREN (+0.94%) Swiss Re - global reinsurer, benefits from increasing AV risk volume
$VRSK Verisk Analytics - data & risk analytics for insurers, AV risk models
$GWRE (-0.05%) Guidewire Software - software solutions for insurance companies, customization for AV policies
$FICO (+2.99%) Fair Isaac - Analytics & risk modeling, increasingly relevant for complex AV data
👉 Favorite: Verisk Analytics ($VRSK
)
Moat through exclusive data pools & analytics. Enabler for almost all insurers. Compounder character, as growing demand for data & models in new markets such as AVs.
Takeaway:
Autonomous driving shifts liability from the driver to the manufacturer or software provider. Insurers need to develop new products, reinsurers and data providers are becoming more important. Munich Re is protecting the industry, Lemonade is testing digital models and Verisk is providing the data intelligence without which no AV insurance can function. Investors will find silent but indispensable winners of the upheaval here.
🛡️ Security & Cybersecurity
Big players:
$PANW (+1.24%) Palo Alto Networks - market leader in network security, focus on cloud & IoT, relevant for connected vehicles
$CRWD (+0.26%) CrowdStrike ($CRWD) - endpoint security, strong platform for AV endpoints and fleets
$CHKP (-0.18%) Check Point ($CHKP) - Security appliances & firewalls, focus on embedded & IoT
$CSCO (+0.11%) Cisco Systems ($CSCO) - Network security + automotive infrastructure
👉 Favorite: Palo Alto Networks ($PANW (+1.24%)
)
moat due to the width of the platform, which extends from the data center to the vehicle. With the $CYBR (+0.76%) -integration, PANW has also covered the topic of identity security. Compounder properties through continuous expansion, high customer loyalty and a strong M&A strategy.
Hidden champions:
$CON (+1.43%) Argus Cyber Security (private, subsidiary of Continental) - specialized in automotive cybersecurity
$Upstream Security (private, Israel) - cloud-based cyber platform specifically for connected vehicles
Karamba Security (private, Israel) - embedded security for control units (ECUs)
$4704 (+0.09%) VicOne (subsidiary of Trend Micro) - AV-specific threat analysis
👉 Favorite: Argus Cyber Security (private, part of $CON (+1.43%)
Continental)
Pioneer in the automotive segment, deep integration in OEMs. Moat through early partnerships and specialization in vehicle architectures.
Shovel manufacturer:
$AKAM (+1.31%) Akamai - Content Delivery & Edge Security, relevant for OTA updates
$FTNT (+0.74%) Fortinet - Network & IoT security, broad base
$ZS Zscaler - cloud-native security for data traffic between AV & cloud
$NET (+1.33%) Cloudflare - infrastructure protection, DDoS protection for fleets & updates
$BB (+3.45%) BlackBerry QNX - Operating system & security framework for automotive
👉 Favorite: BlackBerry ($BB (+3.45%)
)
Moat by QNX, which is already running in millions of vehicles. Strong lock-in with OEMs. Compounder potential if QNX continues to scale as a security operating system for AV architectures.
Takeaway:
Cybersecurity is the nervous system of autonomous driving. Without secure communication, OTA updates and fleet protection, AV is inconceivable. Palo Alto Networks provides the necessary breadth and depth, Argus secures the vehicles themselves, and BlackBerry QNX provides the foundation in the control units. Investors are relying on the invisible gatekeepers of tomorrow's mobility.
⚡ Energy & infrastructure
Big player:
$EBK (+0.15%) EnBW - operator of charging infrastructure in Germany, expansion of fast-charging parks
$SHEL (+0.27%) Shell - massive entry into e-mobility & charging infrastructure, partnerships with OEMs
$BP (-1%) BP - charging and energy infrastructure via bp pulse, global rollout
$TSLA (-2.95%) Tesla ($TSLA) - Supercharger network as AV backbone, potential licensing model
👉 Favorite: Tesla ($TSLA (-2.95%)
)
Moat due to world's largest fast charging network with high availability & own software integration. Compounder, as Supercharger can grow as a service independently of the OEM.
Hidden champions:
$Ionity (private, joint venture of BMW, Mercedes, Ford, VW, Hyundai) - Europe's premium charging network 👉 Access via OEMs such as BMW or Mercedes
$ALLG Allego - listed charging infrastructure operator, focus on Europe
$FAST (+0.11%) Fastned (FAST.AS) - fast charging network in Europe, rapidly growing
$DCFC Tritium DCFC - manufacturer of fast charging stations, globally active
👉 Favorite: Fastned ($FAST (+0.11%)
)
Clear business model as a pure fast-charging operator, strong moat through premium locations & brand perception. Compounder potential via expansion in Europe.
Shovel manufacturer:
$ABBN (+0.3%) ABB - leader in charging hardware & power grid infrastructure
$ENR (+4.25%) Siemens Energy - grid infrastructure & charging hardware, important supplier for energy transition + AV
$SU (+1.75%) Schneider Electric - power distribution, smart grids for charging infrastructure
$6594 (+3.38%) Nidec - motors & drives for e-mobility
$ETN (+1.36%) Eaton - Energy management & charging infrastructure components
👉 Favorite: ABB ($ABBN (+0.3%)
)
Broadly positioned from fast charging hardware to grid technology. Moat due to market leadership & long-standing customer base. Compounder, as electromobility + AV will bring growth for decades.
Takeaway:
Autonomous vehicles don't just need software, they need a reliable charging and energy base. Tesla is securing a massive advantage with its Supercharger network, while hidden champions such as Fastned are setting the pace in Europe. On the shovel side, ABB dominates with its global infrastructure expertise. Investors should not underestimate this sector, as no AV will drive without energy.
🏙️ Mobility services & platforms
Big players:
$UBER (+0.05%) Uber Technologies - ride-hailing, partnerships with AV start-ups (Momenta), robotaxi plans in Munich
$LYFT (+0.18%) Lyft - ride-hailing, own AV programs, cooperations with Aptiv & Motional
$DIDIY (-0.93%) Didi Global - largest ride-hailing network in China, AV research on Didi Autonomous Driving
$9888 (+1.8%) Baidu Apollo - robotaxi operator in China, leading with Apollo Go
$AMZN (+1.99%) Amazon / Zoox - fully autonomous robotaxi, integration into Amazon ecosystem
👉 Favorite: Baidu Apollo ($9888 (+1.8%)
HK, China, HKEX)
Moat through network effects in the world's largest mobility market. Apollo Go has already completed hundreds of thousands of robotaxi journeys. Compounder potential as China aggressively promotes AV.
Hidden champions:
$Momenta (private, China) - L4 autonomy software, partnerships with Mercedes & Toyota, based in Suzhou, China
👉 Access indirectly via investors such as $7203 (+0.42%) Toyota or Mercedes $MBG (+0.68%)
$Motional (joint venture Hyundai & Aptiv, private, USA/South Korea) - Robotaxi tests in the USA
👉 Access via $Hyundai or $APTV (+0.68%) Aptiv
$WeRide (private, China) - Robotaxi & AV bus solutions, based in Guangzhou, China
👉 Investors: Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance
$Cruise (private, USA) - GM subsidiary for robotaxis, based in San Francisco
👉 Access via $GM (+2.93%) General Motors
👉 Favorite: Motional (private, USA/South Korea)
Strong moat through OEM partnerships (Hyundai + Aptiv). Realistic scaling through series integration, compounder potential via global fleet integration.
Shovel manufacturer:
$HTZ (-0.65%) Hertz Global - fleet management, integration of AVs in rental fleets
$SIX2 (+1.11%) Sixt SE - Car sharing & fleet leasing, focus on Europe
$R (+1.81%) Ryder System ($R, USA, NYSE) - fleet services & leasing, AV test integration
$GRAB (+2.85%) Grab Holdings ($GRAB, Singapore, Nasdaq) - Southeast Asian ride-hailing market leader, entry into AV services
$Ola Cabs (private, India) - AV pilot projects in India
👉 Favorite: Sixt SE ($SIX2 (+1.11%)
.DE, Germany, Xetra)
Moat due to premium positioning in Europe, flexible business model (rental, leasing, car sharing). Compounder, as Sixt invests early in fleet integration of AVs and benefits from growing Mobility-as-a-Service market.
Takeaway:
Mobility services are the interface to the end customer. This is where it will be decided whether AVs remain just technology or break through to the mass market. Baidu dominates in China, Motional scores with strong partners in the West, and Sixt provides the platform to bring scalable AVs into everyday life in Europe. Investors who get in early will secure access to the future platform monopolies of mobility.
🔋 Battery & drive
Big player:
$300750 CATL - world market leader for battery cells, supplies almost all major OEMs
$373220 LG Energy Solution - global player, supplier for Tesla, Hyundai, GM
$6752 (+1.71%) Panasonic Holdings - long-standing partner of Tesla, strong in energy storage
$1211 (-0.43%) BYD - integrates battery production and vehicles, pioneer in blade batteries
👉 Favorite: CATL ($300750
SZ, China, Shenzhen)
Moat due to technological leadership and economies of scale, supplies almost all global OEMs. Classic compounder, as batteries are at the heart of every AV fleet.
Hidden champions:
$Northvolt (private, Sweden) - European battery startup, sustainable production, supplies VW and BMW 👉 Access indirectly via VW ($VOW3 (+0.96%) DE, Germany, Xetra) or BMW ($BMW (+0.78%) DE, Germany, Xetra)
$SLDP Solid Power - specialist for solid-state batteries, partnerships with Ford and BMW
$ProLogium (private, Taiwan) - solid-state batteries, pilot projects with Mercedes👉 Access indirectly via Mercedes-Benz Group ($MBG (+0.68%) DE, Germany, Xetra)
$QS QuantumScape ($QS, USA, NYSE) - solid-state batteries, strong focus on future technology
$MOD (+5.05%) Modine Manufacturing (USA, NYSE) - Thermal management for batteries, e-motors and power electronics. Critical for range and safety.
$KULR (+4.51%) Technology (USA, NYSE) - specializes in battery cooling, energy storage and recycling. Still small, but focus on safety makes it interesting in the AV context.
$ZIL2 (-1.02%) ElringKlinger (DE, Germany, Xetra) - supplier of battery packs, housings, seals and fuel cell technology. Supports OEMs in electrification and alternative drive systems.
👉 Favorite: Solid Power ($SLDP
USA, Nasdaq)
Technology leader in solid-state batteries with strong OEM partnerships. Moat through patents and early market entries. Compounder potential through commercialization from 2027+.
Blade manufacturer:
$6594 (+3.38%) Nidec (JP) - leader in electric motors for EVs and AVs
$IFX (+0.07%) Infineon Technologies (DE) - semiconductors for power electronics and battery management
$300450 Wuxi Lead Intelligent (China, Shenzhen) - machines for battery production
$UMI (-0.64%) Umicore (Belgium, Euronext) - cathode materials and recycling
$ALB (+9.52%) Albemarle (USA, NYSE) - Lithium mining and processing
👉 Favorite: Infineon Technologies ($IFX (+0.07%)
DE, Germany, Xetra)
Moat due to market leadership in power electronics, deeply integrated in battery and drive systems. Compounder potential due to growing demand for silicon carbide (SiC) chips for EV and AV applications.
Takeaway:
Battery and drive are the foundation of autonomy. Without powerful energy storage, reliable electric motors and robust power electronics, no autonomous vehicle can be operated economically. CATL dominates cell production, Solid Power is a promise of the future in solid state technology, and Infineon supplies the critical power electronics. Investors who neglect this sector are ignoring the heart of autonomous driving.
🗺️ Maps & Mapping
Big players:
$GOOGL (+2.27%) Alphabet / Waymo (USA, Nasdaq) - HD maps for robotaxis, combined with AI-supported real-time navigation
$9888 (+1.8%) Baidu Apollo (China, HKEX) - leader in AV mapping in China, integrated into Apollo Go
$HERE Technologies (private, based in NL/DE, owners: Audi, BMW, Mercedes and others) - global provider of HD maps, industry standard for many OEMs
$TOM2 (-1.25%) TomTom (Netherlands, Euronext) - specialized in HD maps for AVs, partner of Volvo and Bosch
👉 Favorite: HERE Technologies (private, access via OEMs Audi, BMW, Mercedes)
Moat through global map databases, OEM consortium as backing. Compounder potential, as almost all autonomous vehicles rely on HD maps.
Hidden champions:
$002405 Navinfo Co. Ltd, (China, Shenzhen) - market leader for digital maps in China, partnerships with OEMs - unfortunately not tradable in the EU
$Civil Maps (private, USA) - specialized in AI-supported HD mapping for AVs
$DeepMap (private, USA, acquired by $NVDA (+1.48%) Nvidia) - high-precision mapping, integration with Nvidia Drive
$Mapbox (private, USA) - cloud-based mapping platform, strong in the developer ecosystem
👉 Favorite: NavInfo ($002405
SZ, China, Shenzhen)
Dominance in the Chinese market, regulatory anchoring and partnerships with major OEMs. Moat through market access in China, compounder potential through data growth.
Shovel manufacturer:
$PL Planet Labs (USA, NYSE) - daily earth observation data, basis for dynamic mapping
$HEXA B (+6.38%) Hexagon AB (Sweden, Nasdaq Stockholm) - measurement technology and geodata solutions
$TRMB (+0.72%) Trimble (USA, Nasdaq) - positioning and geospatial data for AV and industrial applications
👉 Favorite: Hexagon AB ($HEXA B (+6.38%)
Sweden, Nasdaq Stockholm)
Moat due to decades of experience in geodata and measurement technology, strong market position in industry and automotive. Compounder potential, as mapping and positioning are indispensable for all AV applications.
Takeaway:
High-precision maps are the nervous system of autonomous driving. Without continuously updated HD maps, vehicles cannot navigate safely. HERE secures a key role through OEM stakes, NavInfo dominates the Chinese market, and Hexagon provides the geospatial bucket technology. Investors should not overlook this sector, as mapping is the invisible foundation on which autonomy works.
Sources: own research, https://www.t-online.de/mobilitaet/aktuelles/id_100901210/iaa-mobility-muenchen-2025-alle-neuheiten-von-audi-bmw-vw-opel.html
https://insideevs.de/features/763886/vorschau-iaa-2025-neuheiten-2026/

Lyft Q2 2025: Record passenger numbers and gross bookings drive EBITDA to all-time high
Introduction & market environment
$LYFT (+0.18%) Inc. published its quarterly results presentation for Q2 2025 on August 6, 2025, reporting record figures for several key metrics. The company's shares closed down 3.27% at USD 14.51 in regular trading, but showed signs of recovery in after-hours trading. This quarter's performance represents a significant improvement over Q1 2025, in which the company missed both profit and revenue forecasts.
Highlights of the quarterly performance
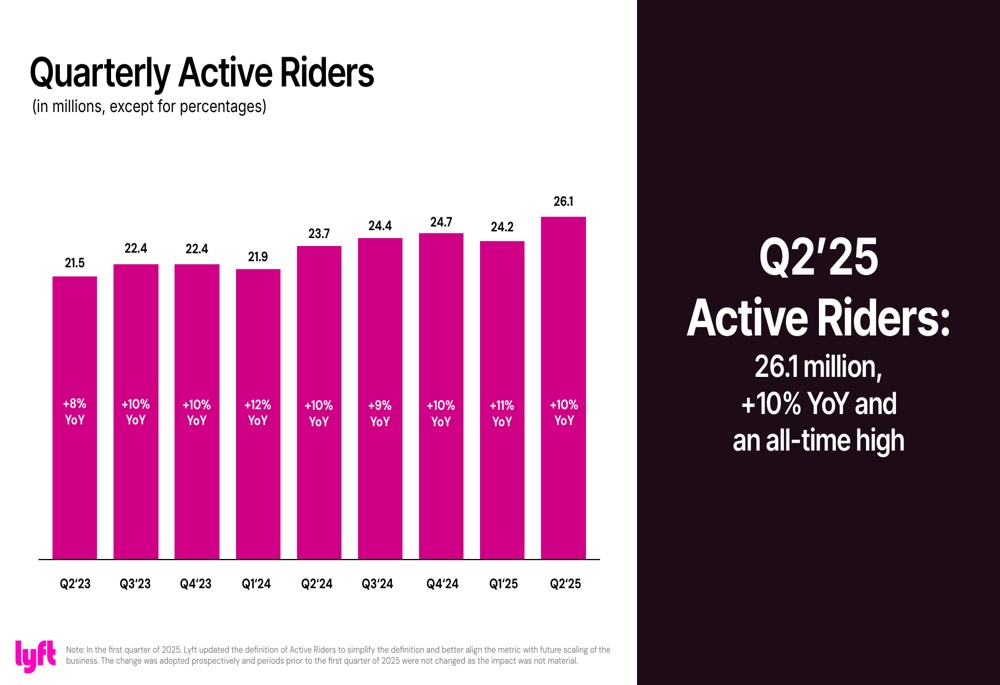
Lyft achieved all-time highs in its key operating and financial metrics in Q2 2025. The company reported 26.1 million active riders, up 10% year-over-year, and completed 234.8 million rides, up 14% compared to the same period last year.
quarterly active passengers:
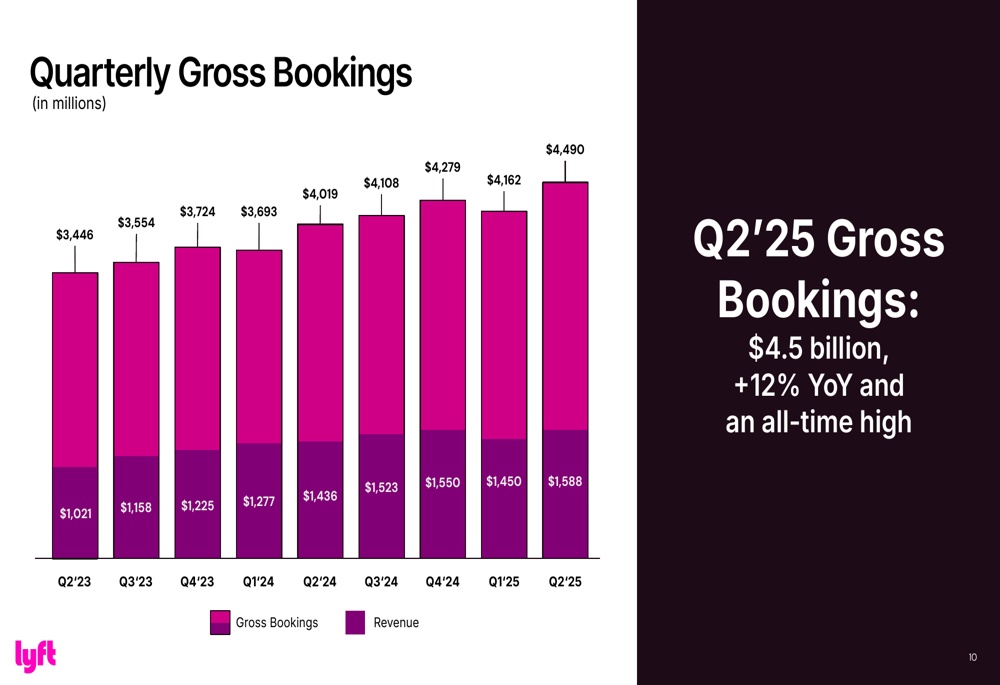
This growth in passenger activity was directly reflected in financial performance, with gross bookings (Gross Bookings) reaching USD 4.5 billion, up 12% year-on-year and also a new all-time high for the company.
Consistent growth in gross bookings:
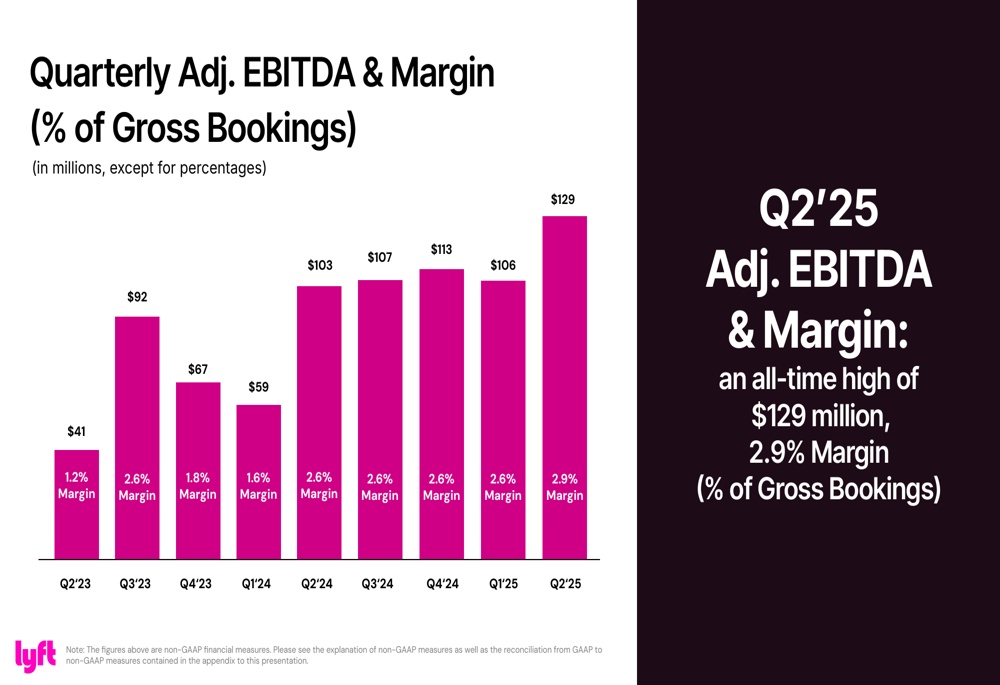
Key profitability figures also showed a significant improvement. Adjusted EBITDA reached USD 129 million (2.9% of gross bookings), which is the highest margin in the company's history. This continues a trend of steady margin improvement over the last two years.
Development of the company's EBITDA:
Of particular note, Lyft generated USD 993 million in free cash flow over the last twelve months, underscoring the company's improved financial stability and operational efficiency.
Significant improvement in free cash flow:
Strategic initiatives
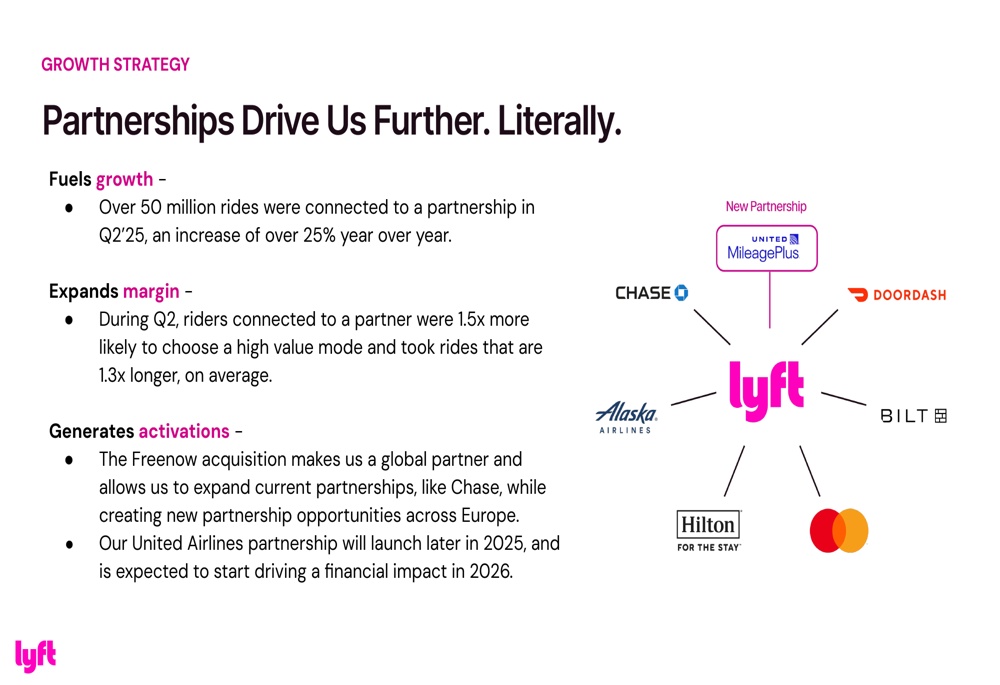
Partnerships have become a cornerstone of Lyft's growth strategy. The company reported that over 50 million rides were attributable to partnerships in Q2 2025, an increase of 25% year-on-year. These partnership-generated rides are proving to be particularly valuable, as passengers referred through partners are 1.5 times more likely to choose high-value transportation and travel 1.3 times longer distances on average.
Company partnership:
Lyft is also expanding its global footprint through strategic acquisitions and partnerships. The acquisition of Freenow opens up new opportunities in Europe, while an upcoming partnership with United Airlines is set to launch in 2025. At the same time, the company is expanding its autonomous vehicle (AV) ecosystem through partnerships along the entire value chain, from autonomous driving technology to fleet management.
Lyft also sees significant growth potential in the US market, pointing out that about two-thirds of the estimated 161 billion annual private rides take place in markets that are currently underpenetrated. The company cited Indianapolis, Nashville and Milwaukee as examples of markets where both driver hours and the number of rides increased by over 20% in the second quarter.
Market opportunities USA:
Operational improvements
Lyft has made significant progress in improving the efficiency of the marketplace, particularly by reducing incentive costs. Total incentives per ride decreased to USD 1.03 in Q2 2025, compared to USD 1.82 in Q2 2023, representing a significant improvement in operational efficiency. The company stated that it is on track to achieve its 2024-2027 target of a 10% annual increase in incentive efficiency.
Trend of improved marketplace efficiency:
Outlook
For Q3 2025, Lyft forecasts gross bookings of approximately USD 4.65 billion to USD 4.80 billion, representing year-on-year growth of 13% to 17%. The company expects adjusted EBITDA of USD 125 million to USD 145 million, which corresponds to an adjusted EBITDA margin of approximately 2.7% to 3.0% of gross bookings.
Company guidance for Q3:
Lyft also reiterated that it is on track to achieve the long-term goals presented at the June 2024 Investor Day. This indicates confidence in the strategic direction despite the highly competitive environment and economic uncertainties.
Source:
investing.com
lyft.com
+ 5
LYFT Q2'25 Earnings Highlights
🔹 Revenue: $1.59B (Est. $1.61B) 🔴; P +11% YoY
🔹 EPS: $0.10 (Est. $0.26) 🔴
🔹 Gross Bookings: $4.49B (Est. $4.50B) 🔴; +12% YoY
🔹 Adj EBITDA: $129.4M (Est. $124.7M) 🟢; +26% YoY
Operational Metrics
🔹 Active Riders: 26.1M (Est. 25.86M) 🟢; UP +10% YoY
🔹 Rides: 234.8M (Est. 236.05M) 🔴; UP +14% YoY
🔹 Dual-app driver preference: +29pts YoY (vs. +6pts YoY)
🔹 Lyft Silver retention rate: ~80%
🔹 Business riders 4x more likely to choose premium ride modes
Other Metrics:
🔹 Adj. EBITDA Margin: 2.9% (vs. 2.6% YoY)
🔹 Net Income: $40.3M; UP from $5.0M YoY
🔹 Net Income Margin: 0.9% (vs. 0.1% YoY)
🔹 Free Cash Flow: $329.4M; UP +28% YoY
🔹 Net Cash from Ops: $343.7M; UP +24% YoY
Guidance – Q3'25
🔹 Gross Bookings: $4.65B–$4.80B; UP +13–17% YoY
🔹 Adjusted EBITDA: $125M–$145M
🔹 Adj. EBITDA Margin (as % of Gross Bookings): 2.7%–3.0%
🔸 Q3 will include two months of Freenow acquisition results
Capital Allocation
🔹 Share Repurchase: 12.8M shares bought back for $200M
CEO & CFO Commentary
🔸 “We delivered off-the-charts performance, resulting in our strongest quarter ever.” — CEO David Risher
🔸 “Our marketplace is thriving, our TAM is expanding with the close of Freenow.”
🔸 “Q2 was another quarter of strong execution with record rides, bookings, and cash flow.” — CFO Erin Brewer
🔸 “We’re ready to accelerate growth and deliver on long-term targets.”
🛡️ Market overview - June 25, 2025
🌍 Macro & markets:
Stock markets rose significantly, supported by a fragile ceasefire between Israel & Iran as well as falling oil prices. Additional tailwind was provided by signals from the Fed, which raised hopes of a summer interest rate cut.
✅ S&P 500 $SPY: +1.11% to 6,092
✅ Nasdaq 100 $QQQ: +1.53% to 22,190
✅ Dow Jones $DIA: +1.19% to 43,089
✅ Russell 2000 $IWM: +1.28% to 2,161
✅ 9 out of 11 sectors up - tech ($XLK +1.8%) ahead, energy ($XLE -1.3%) at the bottom
🚢 Consumer data & corporate news:
✅ Carnival $CCL (+0.65%)
: +6.91% - Strong figures with record sales, high ticket demand & record bookings for 2026. The forecast was raised, despite geopolitical risks the desire to travel remains unbroken.
⚠️ FedEx $FDX (+0.8%)
: After-hours -5%. Weak Asian demand forces 35% capacity cuts on transpacific routes. Full-year guidance lowered, shares down 17% YTD.
🤖 Developments in the robotaxi sector:
✅ Uber $UBER (+0.05%)
: +7.52% - launch of self-driving Waymo vehicles ($GOOG +1.04%) in Atlanta. Waymo with over 1 million autonomous miles & 150,000 paid rides/week.
✅ Lyft $LYFT (+0.18%)
: +6.09% - Analyst upgrade to "Buy", price target raised from $16 to $21.
📰 Other headlines:
⚠️ Fed officials dampen expectations:
- Bostic expects only one rate cut at the end of 2025, points to inflationary pressure from new tariffs.
- Barr confirms cautious stance, Powell signals "willingness to wait"
✅ OpenAI builds up competition from Microsoft & Google:
Own productivity suite announced directly in ChatGPT, including collaboration features.
✅ Anthropic achieves partial success:
AI training on copyrighted books classified as "fair use", piracy trial to follow in December.
✅ Broadcom $AVGO (+1.93%)
: New all-time high - optimism around AI chip pipeline, HSBC raises price target to $400.
✅ Nektar Therapeutics $NKTR (-6.36%)
: Share price doubles after convincing study on eczema drug, up to 90% symptom improvement.
🔎 Summary:
✅ Consumption & travel sector surprise positively
⚠️ Trade & logistics under pressure, especially Asian routes
✅ Robotaxi & AI with further momentum
⚠️ Fed remains cautious, next weeks in focus: tariffs & possible postponement of interest rate hikes
🚗 Lyft (LYFT) - Smidcap top idea & potential turnaround trade
Fundamental highlights
✅ Q1 sales: USD 1.5 billion (+14% YoY)
✅ Net result: USD +2.6 million (previous year: USD -31.5 million)
✅ EPS improved from USD -0.08 to USD +0.01
✅ Active riders: +11% to record figure of 24.2 million
✅ Trips: +16% to 218.4 million
➡ Platform grows strongly operationally, cost efficiency & scaling take effect
Strategic initiatives & outlook
✅ Share buyback program expanded to USD 750 million - signal of confidence to investors
✅ Lyft Silver: Service for senior citizens - new target group with potential
✅ Earnings Assistant: AI tool for better driver retention & earnings optimization
✅ Q2 outlook:
✔️ Ride growth in the mid double-digit range expected
✔️ Gross bookings: USD 4.41-4.57 billion (+10-14% YoY)
Analysts & Catalysts
🚀 TD Cowen upgrade on June 24.:
✅ Upgrade from "Hold" to "Buy"
✅ Price target raised from 16 to 21 USD
✅ Lyft named "best smidcap idea 2025"
✅ Growth driver:
✔️ Focus on smaller markets outside the top 25
✔️ Expansion through FREENOW takeover
✔️ Continuous product innovation (e.g. price fixing)
Chart technique & short-term trading scenario
✅ Breakout above the GD20 & resistance line is in focus
✅ Pivotal point from May 09 serves as an important hedging zone
✅ Consolidation could be complete - new upward wave possible
Conclusion for active traders
🔥 Combination of operational turnaround, expansion, product innovations & analyst upgrade
📈 Break above USD 15-15.50 could ignite a new upward push
🎯 Price target USD 18 in the short term, USD 21 in the medium term according to TD Cowen
What does Lyft actually do? - Summary Q4 Conference
I took part in Lyft's conference call ($LYFT (+0.18%) ) for the 4th quarter and the full year 2024, which I would like to summarize for you.
CEO David Risher announced that 2024 had been a year of "reinvention and industry leadership" for Lyft. The company has reached all-time highs in rides, riders and driver hours. At the end of January, Lyft achieved its highest market share since 2022. The financial results were the best everconfirming the thesis that customer centricity drives profitable growth.
Drivers are choosing Lyft at record ratesand drivers collectively earned nearly 9 billion dollars in 2024. Technological innovations have shortened pick-up times and reduced "prime time" prices. The average number of rides per person has increased and Lyft has the most high-frequency riders in 5 years. The partnership with DoorDash was successful as it resulted in a record number of scheduled rides.
CFO Erin Brewer announced that 2024 was a remarkable year for Lyft. The company exceeded all targets in its multi-year plan. The gross bookings amounted to 16.1 billion dollarsan increase of 17%. By reducing "prime time" pricing and increasing efficiency and cost discipline, Lyft be GAAP profitable for the first time in a full year and generated free cash flow of 766 million dollars dollars.
In the fourth quarter, the number of rides increased by 15% and the number of active riders by 10%, while prices in the US market fell. For the first quarter of 2025 growth in gross bookings of around 10 % to 14 % is is expected. Lyft has also launched a share buyback program in the amount of 500 million dollars. announced.
In addition, the impact of new market participants such as Waymo was also discussed.
It was made clear that Waymo is seen as a company with very impressive technology, especially when it comes to their autonomous vehicles. In San Francisco, however, Waymo was seen as a premium product that is about 20% more expensive than Lyft's services. Despite Waymo's presence in San Francisco, its market market share there has remained stable. It is expected that these new technologies, like Waymo's, will create new demand from which Lyft can also benefit.
In addition, the introduction of autonomous vehicles is being driven forward. Lyft is planning the introduction of AVs in 2025 in collaboration with May Mobility in Atlanta. A partnership with Marubeni was also announced, which will utilize Mobileye's "Lyft-ready" AV technology, starting with a fleet of fleet of 1,000 vehicles in Dallas starting in 2026. AVs are seen as an opportunity to expand the market not as competition to existing rides.
I hope you enjoyed the summary. Basically, however, I am still #TeamUber ($UBER (+0.05%) )

Uber vs LYFT - active customers
In the last 15 months $UBER (+0.05%) gained 29 million active customers per month.
That's more active customers than Lyft has in total. 🚀
LYFT Q4'24 Earnings Highlights:
🔹 Revenue: $1.55B (Est. $1.556B) 🟡; UP +27% YoY
🔹 Gross Bookings: $4.3B (Est. $4.315B) 🟡; UP +15% YoY
🔹 Adj EBITDA: $112.8M (Est. $104.05M) 🟢; UP +69% YoY
🔹 Net Income: $61.7M (Est. $85.80M) 🔴
Q1'25 Guidance:
🔹 Gross Bookings: $4.05B-$4.20B (Est. $4.262B) 🔴
🔹 Adjusted EBITDA: $90M-$95M
Q4'24 Operational Metrics:
🔹 Rides: 219M; UP +15% YoY
🔹 Active Riders: 24.7M (Est. 24.56M) 🟢; UP +10% YoY
🔹 Revenue per Active Rider: $62.7
Strategic Updates:
🔸 Announced $500M Share Repurchase Program for Class A common stock.
🔸 Surpassed all targets set during the Investor Day, achieving record cash flow and margin expansion.
🔸 Lyft continues to outperform on driver preference and achieved industry-best ETAs during Q4.
Management Commentary:
🔸 CEO David Risher: "2024 was a record-smashing year for Lyft, with all-time highs in rides, riders, and service levels. In 2025, we’ll focus on delivering a better rideshare choice for millions."
🔸 CFO Erin Brewer: "We achieved record Gross Bookings, significant margin expansion, and our first full year of GAAP profitability, setting a strong foundation for our multi-year growth plan."
Trending Securities
Top creators this week