
Preface:
hello getquinners,
I researched everything myself in the whitepaper, on the Ethereum site and wrote it myself (no Ki Slop)
so there will be spelling and grammar mistakes in here (don't be mad at me)
I only did the "risks" section with AI because it would be exhausting to work through and think about.
if this is well received here I will gladly make more so leave an impression and now: Have fun with the Ethereum Deep Dive.
ETHEREUM
Ethereum is a decentralized open-source blockchain network and software development platform powered by the cryptocurrency Ether (ETH). Ethereum is the secure, global foundation for a new generation of unstoppable applications.
The Ethereum network is open to everyone: No permission is required. It has no owner and is built and maintained by thousands of people, organizations and users around the world.
Ethereum was founded in July 2015 by Vitalik Butarin, the idea behind Ethereum is simple, while Bitcoin is considered a store of value, Ethereum is intended to provide the infrastructure for the development of digital infrastructure (web3)
There is an open source program called: Smart Contracts.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts let you create decentralized assets and applications (dApps) that work 24/7 globally and without institutions, all you need is electricity and internet!
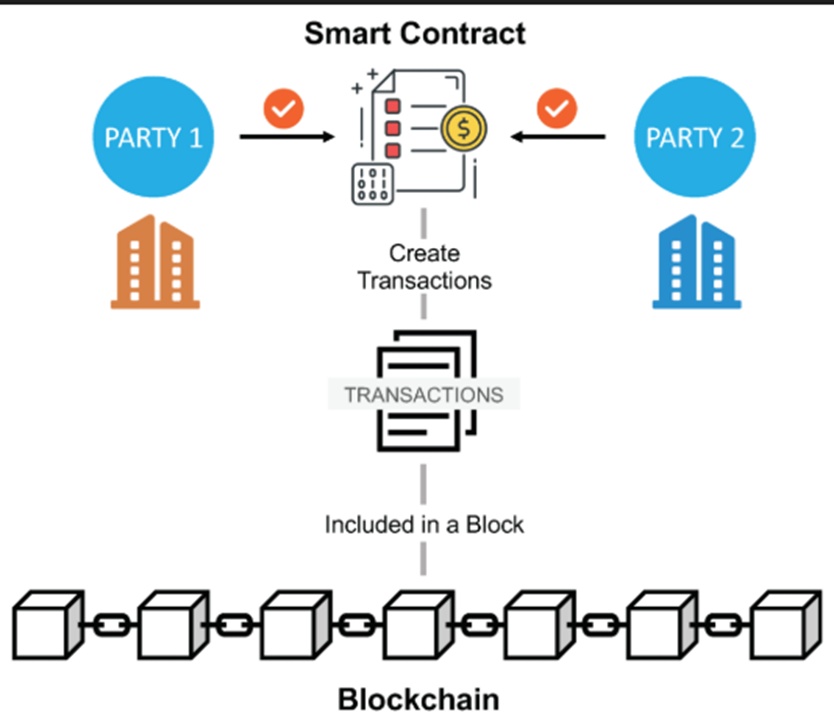
With the help of the Ethereum blockchain, several technical innovations have emerged since 2015, these are the most relevant:
Stablecoins:
Stablecoins are digital currencies whose value is tied to a stable asset, usually a fiat currency such as the US dollar or the euro. This is intended to reduce price fluctuations, as with other cryptocurrencies, in order to make them more usable as a means of payment or store of value.
- Fast, low-cost transfers worldwide: money can be transferred in seconds and often with low fees, even across borders.
- Access without a bank account: Anyone with internet and a wallet can use stablecoins, which is particularly helpful in countries with weak currencies or little bank access.
Non Fundable Tokens (NFTs):
Digital certificates on a blockchain that uniquely assign a unique digital asset to an owner and prove its authenticity.
- Forgery-proof proof of ownership for digital items such as art, music, tickets, in-game items. Less fraud, better tracking, additional features such as access to events or communities.

- NFTs can also store identity, certificates or documents digitally and verifiably, such as proof of education or medical data.
Decentralized finance and gaming apps (DeFi):
DApps are decentralized applications that run on a blockchain and function without a central authority.
Typical examples:
Decentralized financial services (DeFi), games, marketplaces, social apps, all based on open protocols.
Why is this useful?
Operates over a network of many computers instead of a single server. More transparency, autonomy and potentially lower risk of failure as there is no single point of failure
Tokenomics:
Ether:
Ether is the token that powers the Ethereum blockchain, it is responsible for paying transaction fees (also called gas fees) for the network and associated applications, providing stability by paying the staker nodes for the security of the network.
Nodes are the name given to the thousands of computer networks worldwide that have more than 32 Ether tokens and staking to ensure the security of the network (Proof of Stake)
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanismin which it is not computing power but the use of coins that decides who is allowed to create new blocks and confirm transactions. Participants lock their own coins in the network (staking) and thus become validators.
Validators who are selected check transactions, build a block from them and receive rewards in the form of ether.
Max Supply:
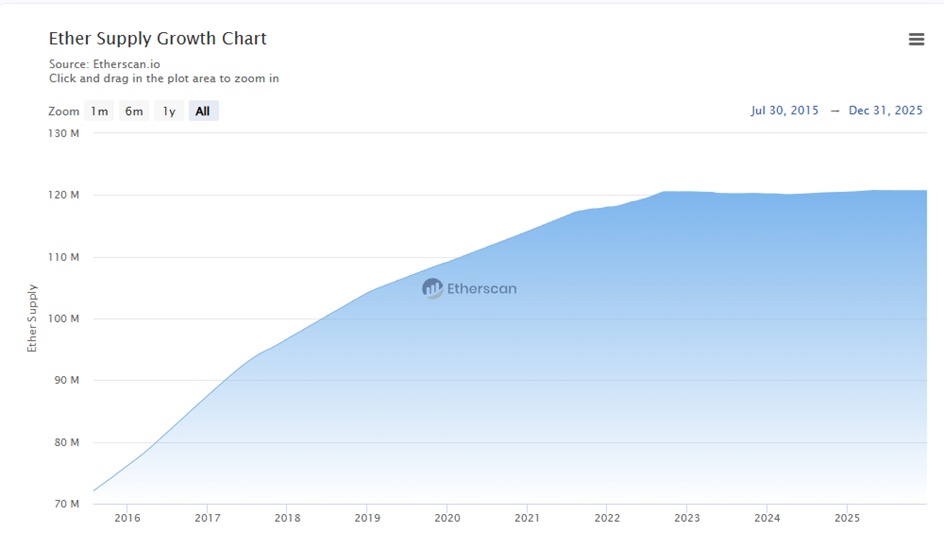
No maximum number of coins, unlike BTC, but there is a burn mechanism that ensures a dynamic shortage
Burns:
every time Ether is sent/used in dApps etc., a small amount is burned (removed) from circulation forever. On active days, more ether is burned than created.
Meaning: the more ether is used, the more is burned, a deflationary system that creates scarcity
Locked tokens:
As of 01.01.2026
- Around 34-36 million ETH are locked in staking in 2025, which roughly corresponds to just under 30% of the circulating supply
- 40% of the supply is locked in smart contracts (DeFi, layer 2, restaking, etc.)
Partnerships:
Important industry alliances
The Enterprise Ethereum Alliance brings together companies such as Microsoft, Intel, Accenture, JPMorgan, Daimler, BP, Visa and others to develop Ethereum standards and use cases for enterprises

Roadmap:
What's next?
Fusaka:
since 03.12.2025 the Fusaka update is running, what exactly it contains is technically difficult to understand and goes beyond the scope, but here is a simplified summary:
The aim is more scalability, efficiency and better developer primitives, especially for layer 2 rollups, plus additional security and protocol improvements,
The main point was the introduction of PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling) so that Ethereum and L2s (blockchains built on Ethereum) can process more transactions more cheaply.


As an investment, Ethereum harbours several blocks of risk: high price volatility, regulatory uncertainty, technical/protocol-related risks, competition from other chains as well as centralization and governance risks.
Price and market risks
- ETH is highly volatile; sharp price declines due to macro events, changes in sentiment or crypto crashes are possible at any time.
Regulatory risks
- Unclear classification (security vs. commodity) and stricter crypto regulations could restrict or make trading, staking offers or DeFi use on Ethereum more expensive.
- National regulations (e.g. on staking, KYC, tax) may make certain business models unattractive and pull capital out of the ecosystem
Technical & protocol risks
- Smart contract bugs, bridge hacks or errors in upgrades (e.g. Fusaka & future hard forks) can lead to losses and damage to trust.
- Long-term issues such as the state size of the chain, possible attack vectors in the PoS system or future quantum computers could undermine security if countermeasures are not taken in good time.
- Strong centralization in PoS staking: If a few players control the majority of validators/staked ETH in the long term, attacks, censorship or political influence would be more realistic and the "decentralized" promise would be broken.
Centralization & staking risks
- A lot of staked ETH is held by a few large staking protocols/exchanges; this creates concentration and governance risks, including coordinated censorship or consensus manipulation.
- Problems or regulation at a dominant staking provider (e.g. Lido, CEX staking) can have systemic effects on the entire network.
Competition and network effect risks
- Faster and cheaper chains such as Solana, Avalanche or other L1/L2 could attract developers, users and liquidity.
- If DeFi, NFTs and new use cases increasingly migrate to other chains, this will weaken fee income, security (less value in the system) and the relevance of Ethereum.

I am convinced of the technical possibility that Ethereum offers as an infrastructure for various layer 2 blockchains such as Base (the blockchain that Coinbase/Circle uses for its stablecoins, for example)
in Germany, we are all living behind the moon and it will take some time before this catches on here... nevertheless, we should not ignore what is going on in the USA and especially Asia, where there is a lot of innovation and advancement of digital infrastructure with the help of ETH
for this reason I am using the dip and have bought a little bit of ETH after the end of this deep dive.
I thank everyone who has read this, if the response is good, I will make the effort and work out the same for another cryptocurrency for you, it was really fun!
Feel free to give feedback, also the other creators, what I could do better!
Happy New Year!








